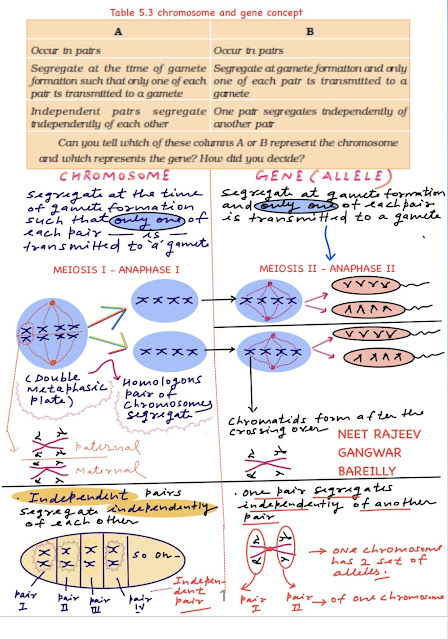
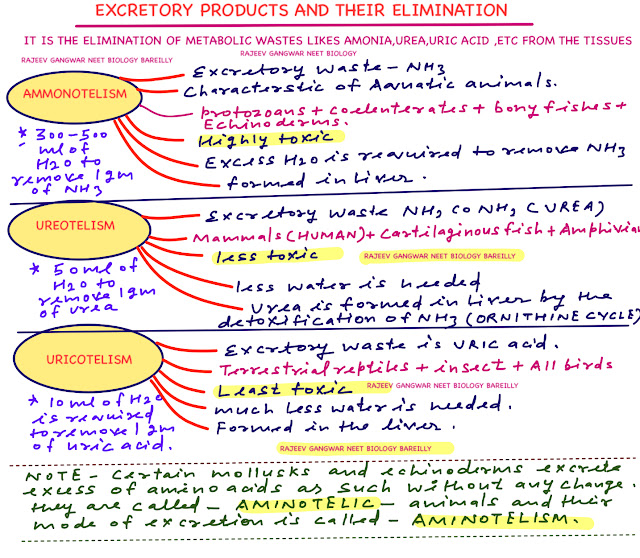
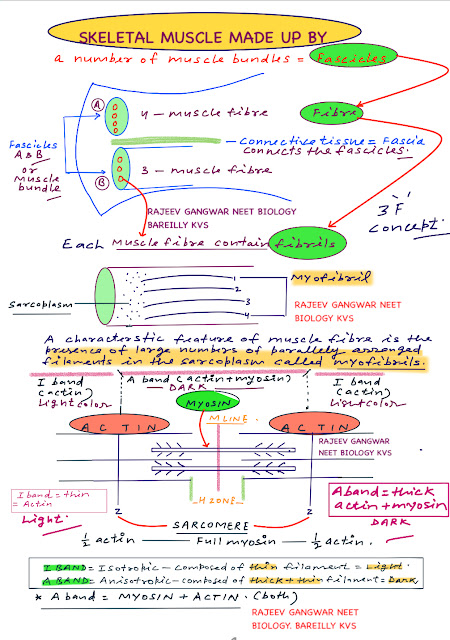
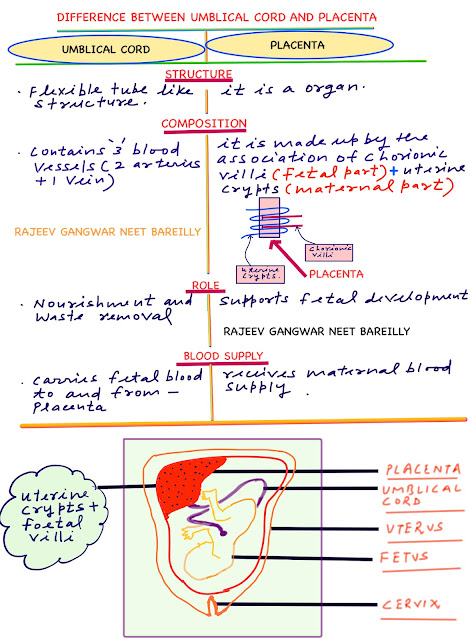
BIOLOGY PREPARATION ON LINE
LEARN BIOLOGY ONLINE , NEET: Lets MAKE IT EASY
Search This Blog
Total Pageviews
Labels
- CLASS XI BIO FOR BRIGHT
- CLASS XII BIO FOR BRIGHT
- AT A GLANCE NEET(BIO TOPIC WISE)/XI SERIES
- CLASS XI
- AT A GLANCE NEET(BIO TOPIC WISE)/XII SERIES
- CLASS XII
- BIO TRICKS #NEET
- CLASS XI CHAPTER WISE QUESTIONS
- BIOLOGY MCQ/NEET FOR PRACTICE
- CLASS X
- HUMAN PHYSIO
- ADOLESCENT EDUCATION PROGRAMME
- CLASS XI CBSE BIOLOGY CHAPTER WISE QUESTIONS 2017
- CYTOLOGY
- KV TEACHERS
- BIOMOLECULES
- CELLULAR RESPI
- EVOLUTION
- GENETICS
- HUMAN REPRODUCTION
- BIOLOGY TEST/CLASS XII
- GREEN SCHOOL PROGRAMME
- MCQ
- Question - Answer
- XI TEST SERIES
Labels
- CLASS XI BIO FOR BRIGHT (39)
- CLASS XII BIO FOR BRIGHT (28)
- AT A GLANCE NEET(BIO TOPIC WISE)/XI SERIES (22)
- CLASS XI (21)
- AT A GLANCE NEET(BIO TOPIC WISE)/XII SERIES (20)
- CLASS XII (17)
- BIO TRICKS #NEET (11)
- CLASS XI CHAPTER WISE QUESTIONS (9)
- BIOLOGY MCQ/NEET FOR PRACTICE (5)
- CLASS X (5)
- HUMAN PHYSIO (5)
- ADOLESCENT EDUCATION PROGRAMME (4)
- CLASS XI CBSE BIOLOGY CHAPTER WISE QUESTIONS 2017 (4)
- CYTOLOGY (3)
- KV TEACHERS (3)
- BIOMOLECULES (2)
- CELLULAR RESPI (2)
- EVOLUTION (2)
- GENETICS (2)
- HUMAN REPRODUCTION (2)
- BIOLOGY TEST/CLASS XII (1)
- GREEN SCHOOL PROGRAMME (1)
- MCQ (1)
- Question - Answer (1)
- XI TEST SERIES (1)
Tuesday, 19 August 2025
Tuesday, 8 July 2025
Friday, 25 April 2025
Saturday, 21 December 2024
CLASS XI LIST OF INVESTIGATORY PROJECT
Thursday, 3 October 2024
Wednesday, 17 July 2024
Saturday, 11 May 2024
Thursday, 14 March 2024
63 most important topics ...must prepared for XII (Biology) 2024-25
1. Polymerase chain reaction
(Full process)
2. Human Genome project.
3. Gel Electrophoresis process.
4. Humulin formation process with diagram.(pro insulin to insulin)
5. DNA fingerprinting process.
6. SCID and ADA deficiency treatment of a girl.
7. CANCER
8. AIDS and Plasmodium life cycle.
9. Post transcriptional modifications.
10. PBr 322 vector.
11. Insertional inactivation (Beta galactosidase)
12. Chromosomal theory of inheritance .
13. RNA interference mechanism.
14. Down,klinefelter and turner syndrome .
15. Lac operon.(with diagram)
16. Sewage treatment plant.(process)
17. Bio active molecules, enzymes functions ( Microbes in human welfare)
18. Biofertilisers.
19. Bio control agents.
20. Biogas plant.
21. Replication,transcription and translation process in detail
22. Genetic code.
23. Transgenic animals and plants examples.
24. Bt cotton mechanism.
25. Logistic and exponential Growth curve and equation.
26. Species Area relationship and graph.
27. Decomposition factors.
28. In situ and Ex situ conservation with examples
29. Human diseases pathogens and symptoms.
30. Immunity and types in detail
31. Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis
32. Types of biodiversity and causes of its loss ( Evil Quartet)
33. Pyramids of Ecosystem
34. Pyramids of Population
35. Pyramids of natural selection
36. Mono hybrid,di hybrid,incomplete dominance,pleiotropy,codominance ,test cross,back cross.Multiple allelism,polygenic inheritance with examples.
37. Theories of evolution (Lamarck, Darwin’s ,hugo de vries)
38. Hershey's chase experiment.
39. Meselson and stahl experiment.
40. Griffith experiment.
41. Drosophila and morgan experiment. (Linkage and recombination)
42. Charging of t RNA. Before translation.
43. Enzymes of biotechnology (functions ).
44.BOD,COD,bioreactors(types)
45. Contraceptive methods(all)
46. Male and female reproductive system.
47. Primary and secondary lymphoid organs.
48. Structure of Antibody molecule.
49. Examples of...mutualism,co extinction,predation, parasitism, Sexual deceit etc
50. Miller urey experiment.
51. Polyembryony and Apomixis.
52. Assisted reproductive technologies.(all)
53. Rice Genome project.
54. Pedigree chart analysis
55. Structure of DNA in detail. (Chargaff rule)
56. Convergent and divergent evolution .
57. Homologous and analogous organs with examples.
58. Darwin's finches and
Australian marsupials (Examples of Adaptive radiation)
59. Hardy Weinberg equilibrium
60. Genetic drift, Gene flow, types of mutations. (Frame shift and point)
61. Stem cell technology.
62.Types of pollination with examples
63 Gene Gun,biolistic, electroporation, etc of how to make cells competent for DNA entry.
Monday, 4 March 2024
Thursday, 11 January 2024
Wednesday, 10 January 2024
Friday, 29 December 2023
Sunday, 3 December 2023
Tuesday, 17 October 2023
Sunday, 15 October 2023
Saturday, 26 August 2023
Sunday, 30 July 2023
Friday, 28 July 2023
Wednesday, 26 July 2023
Saturday, 22 July 2023
Friday, 21 July 2023
Wednesday, 19 July 2023
Sunday, 16 July 2023
Saturday, 15 July 2023
Friday, 14 July 2023
Wednesday, 12 July 2023
Sunday, 9 July 2023
Saturday, 8 July 2023
Friday, 7 July 2023
Thursday, 6 July 2023
Wednesday, 5 July 2023
BOTTLENECK VS FOUNDER EFFECT 2023
|
DESCRIPTION |
Bottleneck Effect |
Founder Effect |
|
Definition |
A sharp
reduction in population size, often due to a catastrophic event or intense
selection pressure. |
A small
group of individuals establishes a new population, resulting in reduced
genetic diversity. |
|
Cause |
Natural
disasters, disease outbreaks, human activities, or sudden environmental
changes. |
Migration,
isolation, colonization, or small group formation. |
|
Population
Size |
Significant
reduction in population size, leading to a small surviving population. |
Start
with a small founding population, which becomes the basis for a new
population. |
|
Effects
on Allele Frequencies |
Random
changes in allele frequencies due to genetic drift. Some alleles may be lost
or become more prevalent than before. |
Limited
number of alleles carried by the founding individuals, leading to a skewed
representation of the original population's genetic makeup. |
|
Genetic
Diversity |
Loss of
genetic variation due to the limited number of survivors, resulting in
decreased diversity and increased genetic drift. |
Limited
genetic diversity due to the small number of individuals in the founding
population. |
|
Examples |
The
cheetah population reduced drastically, leading to reduced genetic diversity. |
One
notable example of the founder effect in India is the Parsi community. The
Parsis are a small ethnic and religious group that migrated from Persia
(modern-day Iran) to the Indian subcontinent around the 8th century. They
settled mainly in the region of Gujarat, particularly in the city of Mumbai
(formerly Bombay).. |
-
List of 20 investigatory project ideas for Class XI based on the NCERT syllabus: 1. Study of the Effect of Different Fertilizers on Plant Gr...
-
LIST OF INVESTIGATORY PROJECT/BIOLOGY/ CLASS XII project report on Human health, food and microbes Ecological study of western ghat ...
-
12 bio project topics 19-20 EASY .. 1. encephalitis 2. stem cells-new avenues of life 3. super bugs for plastic disposal 4. biodive...